Post Anaesthesia Care Unit
Advanced Monitoring Solutions for Post-Operative Patients
Home / PACU
PACU
After surgery, it is essential that clinicians become aware of patient deterioration and respiratory abnormalities as soon as possible so as to quickly administer appropriate treatment. Challenged by frequently low clinician-to-patient ratios and the intermittent nature of many current monitoring modalities, clinicians sometimes identify deterioration when it may be too late. Masimo’s integrated oxygenation and perioperative monitoring solutions help clinicians care for post-operative patients at risk of respiratory depression and other unforeseen complications.
Noninvasive and Continuous Respiratory Rate
Noninvasive and Continuous Respiratory Rate

The Anaesthesia Patient Safety Foundation (APSF) recommends continuous oxygenation and ventilation monitoring for all patients receiving opioid-based pain medications.1 However, current methods of respiration rate monitoring may be limited by shortcomings related to accuracy and patient tolerance.2,3
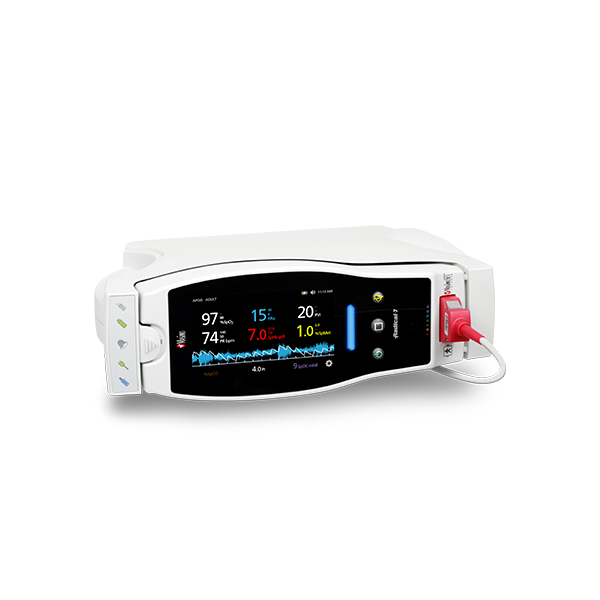
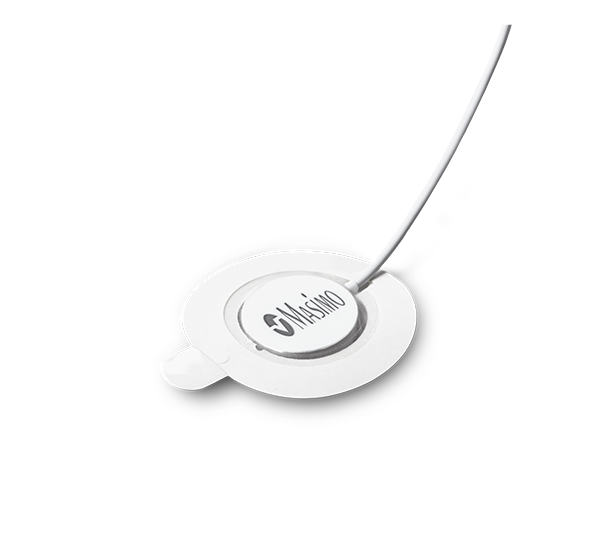
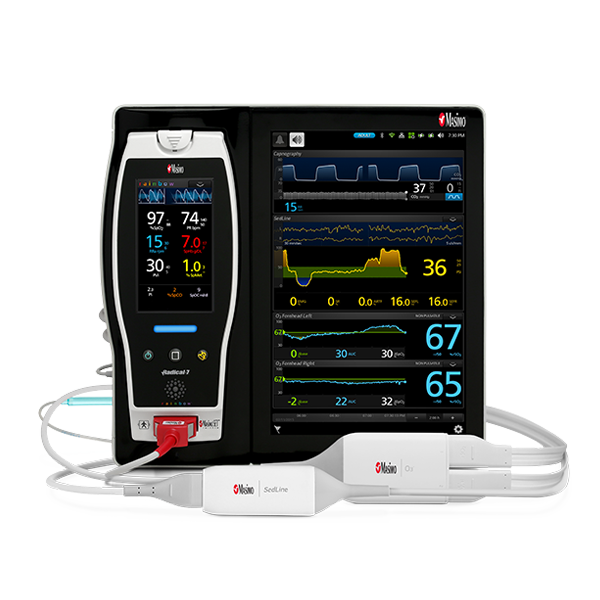
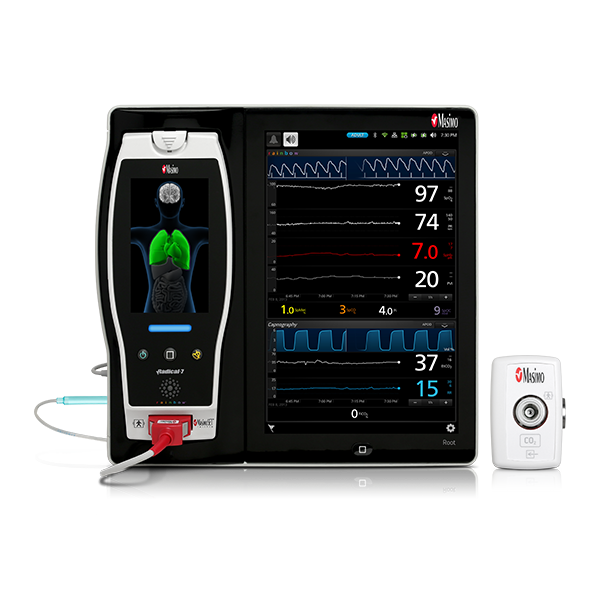
rainbow Acoustic Monitoring® is a noninvasive and continuous method of monitoring respiratory rate in post-operative patients that has the benefit of higher patient compliance.4,5 A Respiratory Acoustic Sensor applied to the patient’s neck – such as the small, lightweight RAS-45 – detects acoustic signals produced by turbulent airflow in the upper airway that occurs during inhalation and exhalation. Signal processing algorithms convert the acoustic patterns into breath cycles to calculate respiratory rate, which is displayed as a continuous RRa® measurement and real-time acoustic waveform on Masimo Pulse CO-Oximeters®.
While Masimo offers capnography solutions, rainbow Acoustic Monitoring may be more appropriate for some patients.
Comprehensive Oxygenation Monitoring
Comprehensive Oxygenation Monitoring
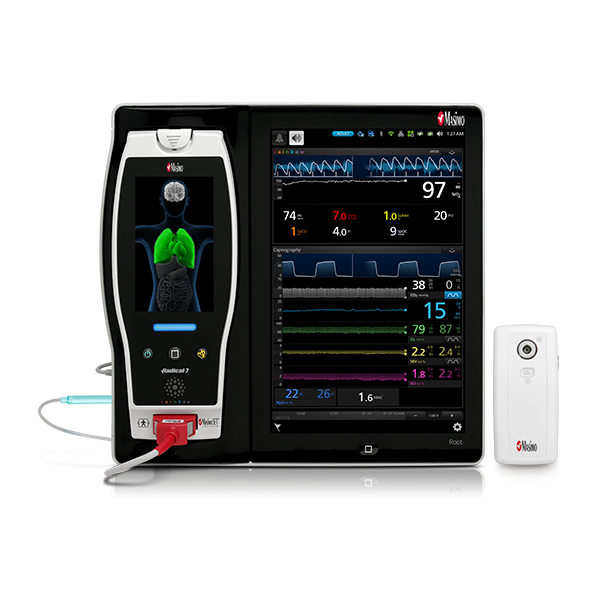
In addition to continuous respiratory rate monitoring with RRa, Masimo offers continuous SpO2 monitoring with SET® Measure-through Motion and Low Perfusion™ pulse oximetry. Integrating both continuous measurements into a single device not only empowers clinicians with more information regarding a patient’s oxygenation, but also reduces the footprint needed for multiple monitors in a crowded PACU.
Performance During Motion and Low Perfusion8
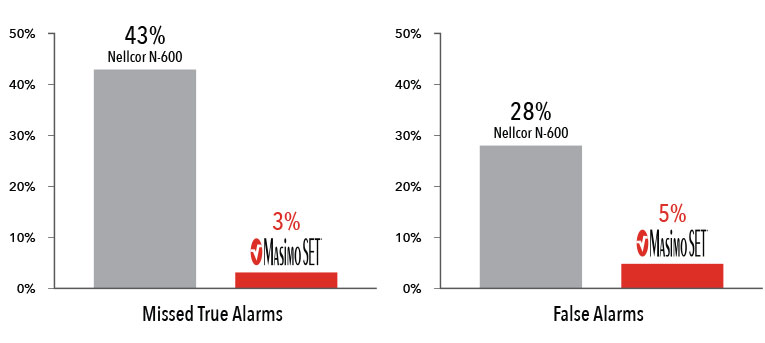
Masimo SET® had 3% missed true alarms and 5% false alarms versus 43% and 28%, respectively, using competitor technology.8
Results shown are calculated by combining sensitivity and specificity outcomes of machine-generated and
volunteer-generated motion.
Two separate studies found that Masimo SET® pulse oximeters detected approximately 10 times more true events than other “Next Generation” pulse oximeters studied.6,7 In another study comparing the ability of three pulse oximetry technologies to detect hypoxic events, Masimo SET® pulse oximetry demonstrated the highest sensitivity and specificity during induced conditions of motion and low perfusion.8
A More Complete Picture of the Brain
A More Complete Picture of the Brain
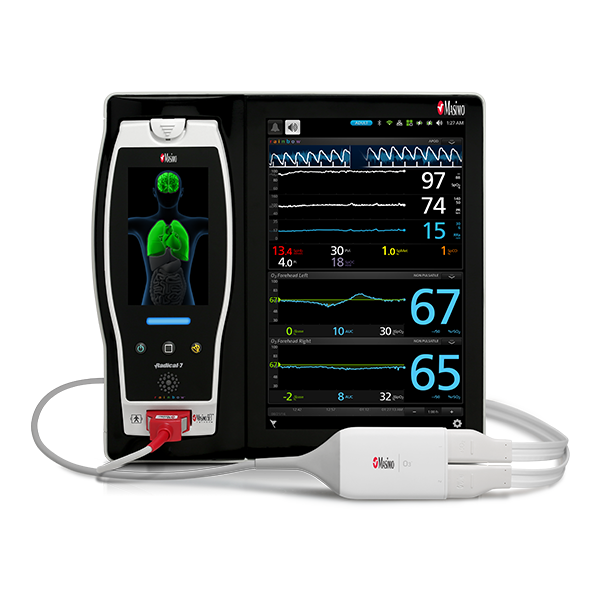
In addition to respiratory rate and pulse oximetry, Masimo also offers solutions for brain function monitoring and cerebral oximetry.
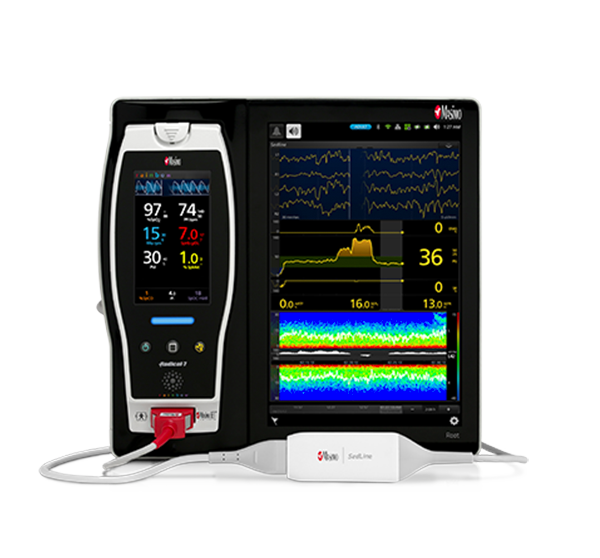
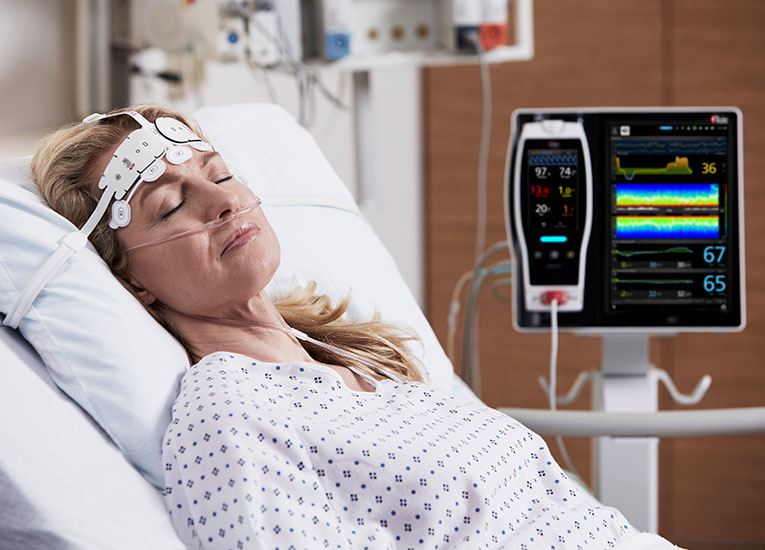
As in the ICU, in the PACU subjective assessments of brain function may be unobtainable while patients are weaned from anaesthesia and sedation.9 Next Generation SedLine® brain function monitoring may be useful in helping clinicians assess the sedation state of the brain, with the bilateral acquisition and processing of four leads of electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. Next Generation SedLine features an enhanced processed EEG index (PSi) with less susceptibility to EMG interference and improved performance in low power EEG cases, as well as an optional enhanced Multitaper Density Spectral Array (DSA).
Next Generation SedLine can be used simultaneously with O3® regional oximetry on the Root® platform for a more complete picture of the brain during patient recovery. O3 may help clinicians monitor cerebral oxygenation in situations in which pulse oximetry alone may not be fully indicative of the oxygen in the brain.
Advanced Patient Monitoring and Connectivity Platforms
Advanced Patient Monitoring and Connectivity Platforms
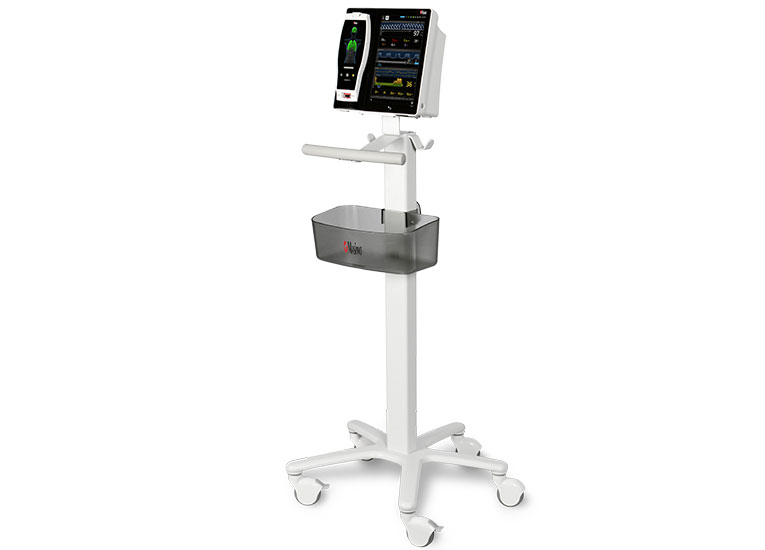
Masimo’s oxygenation and perioperative monitoring solutions are available together on Root, a highly customisable, expandable patient monitoring and connectivity platform that occupies a minimal footprint in the PACU. Compact yet powerful, Root provides multiple high-impact, innovative measurements on a single platform, providing clinicians with more information in one place.
Iris Gateway™ and Iris® ports in Root facilitate automated data transfer from Root and multiple standalone third-party monitors — such as IV pumps, ventilators, and anaesthesia machines – to hospital EMRs, which may reduce the likelihood of transcription errors10 or incomplete case records.
Measurements
Measurements
PACU Solutions
References:
- 1.
The Joint Commission Sentinel Event Alert. Issue 49, August 8, 2012. http://www.jointcommission.org/assets/1/18/ SEA_49_opioids_8_2_12_final.pdf
- 2.
Ramsay MAE et al. Anesth Analg. 2013 Jul;117(1):69-75.
- 3.
Applegate RA et al. Anesth Analg. 2016;122(4):1070-8.
- 4.
Macknet MR et al. Anesthesiology. 2007;107:A84. (abstract).
- 5.
Goudra BG et al. Open J Anesthesiol. 2013; 3:74-79.
- 6.
Hay WW. J of Perinatol, 2002;22:360-36.
- 7.
Barker SJ. Anesth Analg. 2002;95(4):967-72.
- 8.
Shah N. et al. J Clin Anesth. 2012 Aug;24(5):385-91.
- 9.
Barr, Juliana et al. Critical Care Medicine 41, no. 1 (2013): 263-306.
- 10.
The Value of Medical Device Interoperability. West Health Institute. 2013.
RESOURCES
For professional use. See instructions for use for full prescribing information, including indications, contraindications, warnings, and precautions.
PLCO-002024/PLM-11356A-0718